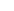What does a Business Intelligence Specialist do
Business Intelligence Specialists have become indispensable in a data-driven world. They are experts in collecting, analyzing, and visualizing data, helping organizations make data-driven decisions. By identifying trends, patterns, and anomalies in data, they make complex information accessible to management and operational teams.
What does a Business Intelligence Specialist do?
A Business Intelligence (BI) Specialist translates raw data into strategic insights. They work with modern tools like Power BI, Tableau, Qlik, SQL, and Python to integrate data from various systems and convert it into valuable insights. The role combines technical skills with business acumen and strong communication abilities.
Key tasks and responsibilities:
- Data collection: Gathering data from diverse sources such as relational databases, cloud platforms, spreadsheets, and APIs.
- Data processing: Cleaning, structuring, and transforming raw data into a usable dataset for analysis.
- Data visualization: Developing and maintaining dashboards, reports, and interactive visualizations that clarify key KPIs and trends.
- Data analysis: Conducting analyses to measure performance, detect anomalies, and make predictions using historical data.
- Collaboration: Aligning with teams such as finance, marketing, sales, and operations to understand what information they need for decision-making.
- Process optimization: Continuously improving BI processes, data pipelines, and automations to enhance speed, reliability, and scalability.
Skills and competencies
A good Business Intelligence Specialist combines analytical insight, technical proficiency, and communication skills. Knowledge of SQL, ETL processes, data warehousing, and BI tools is essential. Curiosity, problem-solving ability, and a proactive mindset are also important to truly help organizations move forward.
BI Specialist: a key role in modern organizations
Organizations are increasingly investing in data analysis to gain a competitive advantage. As a result, demand for Business Intelligence Specialists is growing rapidly. Whether it's improving customer satisfaction, optimizing logistics processes, or identifying commercial opportunities — the BI Specialist plays a key role.

Job Profile of a Business Intelligence Specialist
A typical job profile of a Business Intelligence Specialist includes:
- A relevant academic degree, such as computer science, business administration, mathematics, data science, or another analytical field.
- In-depth experience with BI tools such as Power BI, Tableau, Qlik Sense, Looker, or similar visualization tools. Experience in dashboard development and report building is essential.
- Knowledge of SQL is indispensable, supplemented by experience in programming languages such as Python, R, or DAX for advanced data analysis and automation.
- Proficiency in data modeling, including knowledge of dimensional models (such as star and snowflake schemas).
- Understanding of ETL processes (Extract, Transform, Load) and experience with tools such as SSIS, Informatica, or Apache Airflow.
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills, combined with the ability to identify and explain trends and anomalies in data.
- Excellent communication skills, particularly the ability to make complex data insights understandable for non-technical stakeholders such as managers and executives.
- Experience with project-based work, agile/scrum methodologies, and operating in multidisciplinary teams.
- Affinity with data quality, data governance, and security, given the growing importance of reliable and secure data infrastructures.
Importance of the role in modern organizations
In a world where data plays an increasingly significant role, the position of Business Intelligence Specialist is becoming more crucial. This specialist helps organizations stay competitive by providing strategic insights, optimizing operational processes, and analyzing customer behavior. The demand for BI professionals has also significantly increased in government institutions, healthcare organizations, and non-profits.
Growing emphasis on soft skills and domain knowledge
In addition to technical skills, more value is being placed on soft skills such as collaboration, adaptability, and critical thinking. Domain-specific knowledge – for example in finance, logistics, or marketing – is also becoming more important. This allows the BI Specialist to better address the information needs within a specific organizational context.
A future-proof career choice
The role of Business Intelligence Specialist offers excellent career prospects. Due to the growing importance of data across every sector, this is a future-proof career with plenty of opportunities to further specialize, for example toward data engineering, data science, or analytics consultancy.

A day in the life of a Business Intelligence Specialist
A Business Intelligence Specialist is much more than someone who analyzes data. He or she is the silent force behind data-driven decisions, the bridge between IT and business, and the designer of insights in dashboards. But what does a typical workday really look like?
08:00 – Starting the day with data: “Are all systems awake?”
The workday usually begins with a fresh cup of coffee and a quick glance at the dashboards. Did the automated reports come through correctly? Are there any error messages in the ETL processes (Extract, Transform, Load)?
The BI Specialist checks whether data feeds from various sources — such as CRM systems, financial tools, or production databases — have been properly ingested. Any issues are immediately addressed or reported to the data teams.
“I start each day with a health check. A dashboard that hasn't refreshed or a suddenly empty chart can have major consequences for decision-making later in the day.”
09:00 – Stand-up with the team: quick alignment
In many organizations, the BI Specialist works within a scrum or agile team. During the daily stand-up, the following is briefly discussed:
- What was done yesterday?
- What is the focus for today?
- Are there any blockers?
The BI team coordinates with data engineers, product owners, and sometimes directly with business stakeholders.
09:30 – Deep dive: building a dashboard
After the stand-up, the real work begins: building new dashboards or improving existing ones. For example, today’s task is to create a sales performance dashboard for the commercial team.
The BI Specialist:
- Translates functional requirements into technical specifications
- Builds visualizations in tools like Power BI, Tableau, or Looker
- Ensures logical filters, drill-downs, and intuitive UX
It’s not just about looks — it’s about being understandable and usable.
11:30 – Validating, testing, and perfecting
A dashboard without reliable data is like a compass that’s lost its north. That’s why the BI Specialist thoroughly tests all calculations. Does the revenue per region match the source system? Are there strange spikes or drops that indicate data pollution?
Sometimes this means diving into the SQL code, checking if all joins make sense, or realigning with the data engineer.
“Trusting data is good, but validating it is better. One wrong filter can lead to a million-dollar mistake.”
12:30 – Lunch break: time to recharge
Time to relax. Some take a walk, others head to the company cafeteria or eat with colleagues. Stepping away from the screen helps stay fresh for the second half of the day.
13:00 – Stakeholder meeting: listening, probing, and advising
In the afternoon, there’s often a meeting with colleagues from other departments — from HR to marketing and finance. A good BI Specialist knows how to listen and ask the right questions. What does the business really want to know? Why? And how often?
Such meetings reveal:
- Which KPIs truly matter
- How users want to view the data
- Which data fields are essential (and which are unnecessary)
Sometimes it becomes clear that the underlying data model needs adjustments first.
14:30 – Improving data models and processes
The afternoon allows time for technical deep dives. The BI Specialist works on optimizations such as:
- Speeding up data loads
- Normalizing datasets
- Setting up new data models for more scalability
This usually happens in collaboration with data engineers or within the cloud environment (Azure, AWS, Google Cloud).
16:00 – Sharing knowledge: mini-training for colleagues
Many BI professionals enjoy helping colleagues make more use of data themselves. Today, a short training is scheduled for the marketing team: how to use filters in Power BI, how to set alerts, and how to interpret a trend.
“The greatest impact isn’t just made through dashboards, but by teaching others how to derive insights from data themselves.”
17:00 – Review and preparation for tomorrow
The day ends with a review of new data requests. What has come in? Are there any quick wins? What should go on the backlog? Sometimes there’s a quick check-in with a product owner or manager about the roadmap.
A quick glance at the inbox, updating documentation in Confluence or SharePoint — and then it’s time to close the laptop.
Conclusion: it’s never “just” an office day
A BI Specialist has a varied workday that combines technical depth, analytical thinking, and collaboration. No two days are the same, because every data question is unique. From building dashboards to training colleagues, and from data validation to business advising — the BI Specialist is the central hub of data-driven working.
Interested in a role like this? Check the current job openings at DataJobs.nl and find your place in the world of Business Intelligence.

Which tools does a Business Intelligence Specialist use
Which Tools Does a Business Intelligence Specialist Use?
Business Intelligence (BI) is a rapidly evolving field where specialists use a wide range of tools to collect, analyze, visualize, and transform data into valuable insights. Below is an overview of the key tools and technologies used by modern BI specialists.
ETL/ELT Tools (Extract, Transform, Load)
To process data, BI specialists use both traditional ETL tools and modern ELT approaches. ETL moves data after transformation, while ELT first loads data into the data warehouse and then transforms it. Popular tools include Apache NiFi, Microsoft SSIS, Talend, and cloud-native solutions like Fivetran, dbt (data build tool), and Azure Data Factory. These tools automate the retrieval of data from various sources, cleaning, enrichment, and loading into data lakes or data warehouses.
Data Analysis Tools
BI specialists analyze data using programming languages and statistical tools. SQL is the standard language for querying relational databases and is indispensable for data queries. Python and R are used for in-depth data analysis, statistical computations, and machine learning. Popular libraries include pandas, NumPy, scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and ggplot2. Python, in particular, is growing in popularity among data science teams due to its flexibility and large community.
Data Visualization Software
BI is about making complex data understandable. Visualization tools such as Tableau, Power BI, Looker, and Qlik Sense are crucial for building dashboards, interactive reports, and self-service analytics. They support data storytelling and highlight trends, patterns, and anomalies. Thanks to integrations with cloud warehouses, these tools increasingly offer real-time data visualization.
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
Business Intelligence relies on dependable data storage. Specialists use relational databases like Microsoft SQL Server, PostgreSQL, and MySQL, as well as NoSQL solutions such as MongoDB and Cassandra for unstructured data. Additionally, cloud-based databases like Amazon Aurora and Google Cloud SQL are gaining popularity due to their scalability, reliability, and seamless integration with other data solutions.
Business Intelligence Platforms
For organizations seeking an all-in-one solution, platforms such as SAS Business Intelligence, IBM Cognos, Oracle Analytics Cloud, and Microsoft Fabric offer comprehensive functionality. They support reporting, dashboards, data modeling, planning, and advanced analytics. Modern platforms increasingly integrate augmented analytics and AI-driven recommendations to proactively deliver insights to users.
Data Warehousing & Lakehouse Tools
BI specialists store data on powerful storage platforms. Popular cloud-based data warehousing tools include Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, Snowflake, and Microsoft Synapse Analytics. For organizations seeking flexibility, the lakehouse concept — with tools like Databricks — offers a hybrid solution combining the scalability of data lakes with the reliability and structure of data warehouses. This model enables faster and more manageable analysis of large datasets.
Data Modeling Tools
To structure data, BI specialists use data modeling tools such as Erwin Data Modeler, IBM InfoSphere Data Architect, SAP PowerDesigner, and dbt. Dbt, in particular, is popular in modern data stacks due to its focus on transparency, reusability, and version control of SQL models. These tools help create robust and scalable data models that form the foundation of reliable BI reporting.
Collaboration and Project Management Tools
BI teams are increasingly working cross-functionally and agile. Tools such as Microsoft Teams, Slack, Jira, Asana, and Confluence support collaboration, task management, and documentation. Additionally, version control via Git and CI/CD pipelines are used to manage code, data models, and dashboards, ensuring a structured and controlled development environment.
In Conclusion
The toolkit of a modern Business Intelligence Specialist is broad and constantly evolving. Whether it's data extraction, modeling, analysis, or visualization: the right combination of tools determines the effectiveness of a BI strategy. Organizations that invest in a future-proof BI stack not only generate insights but also create a solid foundation for data-driven decision-making.

What does a Business Intelligence Specialist earn
The salary of a Business Intelligence Specialist varies significantly depending on experience level, industry, and organization size:
- Junior BI Specialist (0–2 years of experience): typically earns between €2,800 and €4,000 per month.
- Mid-level BI Specialist (3–5 years of experience): receives an average salary between €3,750 and €6,500 per month.
- Senior BI Specialist (5+ years of experience): can expect a monthly income of €6,000 to €7,500 or more, depending on expertise, certifications, and responsibilities.
In some cases, for example within large international organizations or in highly specialized niches, the salary for senior specialists can even exceed €8,000 per month.
Career Path and Growth Opportunities as a Business Intelligence Specialist
Career Path and Growth Opportunities for Business Intelligence Specialists
A career as a Business Intelligence (BI) Specialist offers a wide range of growth opportunities. This role is ideal for professionals who enjoy working with data and are looking for a dynamic field where analysis, strategy, and technology converge.
Advancing to Senior or Management Roles
As you gain more experience and further refine your skills in data analysis, dashboarding, and data visualization, you can progress to more senior positions such as Senior BI Specialist or BI Lead. In these roles, you take on greater responsibility in leading projects and advising stakeholders.
For those with management ambitions, there are excellent prospects. For example, you can advance to roles such as Business Intelligence Manager, Data Architect, or even Chief Data Officer. In these roles, you are responsible for shaping data strategy and generating insights that directly contribute to business operations and organizational growth.
Specializing by Sector or Technology
BI Specialists can also deepen their expertise in a specific industry, such as healthcare, retail, logistics, government, or financial services. Each sector has its own data structures, reporting requirements, and challenges, offering interesting specialization opportunities.
Additionally, you can set yourself apart by specializing in specific tools and technologies such as Power BI, Tableau, Qlik, SQL, Python, or cloud platforms like Azure and AWS. This technical expertise can further strengthen your position in the job market and increase your value as a specialist.
Working as an Independent BI Consultant
Another path is building a career as an independent consultant or advisor. Many experienced BI Specialists choose to work as freelancers, using their expertise for various clients. This offers greater flexibility, a diverse range of tasks, and often attractive compensation models.
Continuous Learning and Development
The world of data and analytics evolves rapidly. Therefore, ongoing education is essential. Think of obtaining certifications, attending training sessions, and staying up to date with trends such as data governance, artificial intelligence (AI), and predictive analytics. Those who continue to develop themselves increase their chances of a successful and sustainable career in Business Intelligence.
In short, the role of Business Intelligence Specialist is an excellent starting point for a versatile career in data and analytics. Whether you choose specialization, leadership, or independence – the growth opportunities are plentiful.

Training and Certification for Business Intelligence Specialists
To be successful as a Business Intelligence (BI) Specialist, it is essential to continuously invest in your knowledge and skills. The world of data is evolving rapidly, with new tools, techniques, and insights emerging at a fast pace. In addition to a relevant academic background — such as computer science, business administration, or data science — you can enhance your professional development with specialized BI certifications and practical courses.
These programs not only help you deepen your technical skills, but also strengthen your position in the job market. Employers are increasingly valuing verifiable certifications when hiring BI professionals. Some popular and up-to-date certifications and courses include:
Certified Business Intelligence Professional (CBIP)
Offered by TDWI (Transforming Data With Intelligence), this is a leading certification that confirms broad and in-depth knowledge of BI concepts, methodologies, and applications. The CBIP is particularly appealing to experienced professionals who want to emphasize their seniority and expertise. The certification focuses on areas such as analytics, data integration, data warehousing, and information management.
Tableau Desktop Specialist and Tableau Certified Associate
These certifications, developed by Tableau, focus on validating your skills in using their powerful visualization tool. The Desktop Specialist certification is ideal for beginners and confirms that you possess the fundamental knowledge. The Certified Associate goes a step further and requires deep insight into data visualization, dashboards, and data connectivity. Tableau remains a popular choice for organizations that prioritize visual storytelling and interactive dashboards.
Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate (Power BI)
Power BI is one of the most widely used tools for data visualization and analysis, especially in Microsoft environments. This official Microsoft certification focuses on translating data into actionable insights through dashboards, reports, and visualizations. You will learn how to optimally use Power BI for data modeling, query building, and creating scalable BI solutions.
Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
This hands-on course, developed by Google, is ideal for beginners and career changers who want to quickly build a solid foundation in data analysis. You will work with tools such as spreadsheets, SQL, R, and Tableau, and gain insight into the full data analysis cycle. This certification is also popular due to its practical applicability and accessibility through online learning platforms.
IBM Data Analyst Professional Certificate
This certification focuses on developing practical skills in analyzing and visualizing data using tools like Python, Excel, SQL, and Jupyter Notebooks. The course emphasizes hands-on experience, making it especially suitable for professionals looking to retrain or deepen their expertise in data analysis practices.

Benefits of Certification for BI Specialists
Earning BI certifications offers multiple benefits. You stand out in the job market, remain relevant in a dynamic field, and increase your confidence in your role. It also shows potential employers or clients that you invest in your own development and possess up-to-date, validated knowledge.
Keep Learning, Keep Growing
Whether you're at the beginning of your career or have been active in the data world for years, pursuing education and earning certifications is a powerful way to accelerate your career as a Business Intelligence Specialist. Combine this with practical experience, and you’ll be well-positioned to help organizations extract valuable insights from data.
Networking and Industry Organizations
TDWI, DAMA and Other Industry Organizations
For anyone serious about building a career in Business Intelligence, it is essential to stay actively engaged with leading industry organizations such as TDWI (Transforming Data With Intelligence) and DAMA (Data Management Association). These organizations offer a wealth of up-to-date knowledge, insights, and networking opportunities that are indispensable for BI professionals who want to stay ahead.
By becoming a member of TDWI or DAMA, you gain access to high-quality content, whitepapers, certification programs, webinars, and conferences focused on the latest trends and best practices. Topics include data governance, data warehousing, data architecture, AI integration, and self-service BI solutions. This type of knowledge is not only valuable for your daily work but also helps you add strategic value within your organization.
Moreover, active participation in industry organizations increases your professional visibility. By attending events, joining panels, or speaking at conferences, you position yourself as an expert in your field. This opens doors to new collaborations, projects, and career opportunities.
Online Networks for Business Intelligence Professionals
In addition to formal organizations, building and maintaining an online network is a powerful way to stay informed and position yourself as a BI specialist. Platforms such as LinkedIn, specialized Slack groups, online communities, and forums offer an accessible way to connect with other professionals in the world of data analysis, data engineering, and data science.
Participating in discussions, sharing insights, or publishing your own articles and analyses on social media contributes to your visibility within the industry. Regular interaction with peers often leads to the exchange of best practices, discussion of tools and techniques, and the discovery of new developments such as the use of generative AI, cloud-based BI platforms, or data mesh architectures.
Additionally, these networks often lead to opportunities for collaborations, freelance projects, or even new jobs. For those exploring growth opportunities or a transition to a different role within the BI domain, an active online network is almost as valuable as a strong resume.

Impact and societal relevance
The Societal Impact of a Business Intelligence Specialist
A Business Intelligence Specialist plays a key role within modern organizations. This professional is responsible for translating large volumes of raw data into clear, actionable insights. In doing so, they not only contribute to better decision-making and more efficient processes, but also to increasing the societal relevance of an organization.
From Data to Strategic Value
Today, companies have access to enormous amounts of data. A Business Intelligence Specialist knows how to analyze and visualize this data in smart ways, making trends, bottlenecks, and opportunities visible. This enables strategic decision-making, improves customer satisfaction, and makes organizations more agile in a rapidly changing market.
Impact on Sustainability and Efficiency
The impact of business intelligence goes beyond the commercial world. Consider, for example, the optimization of production chains: by using raw materials more efficiently, organizations can contribute to sustainability goals. Less waste, lower energy costs, and smarter logistics lead to both ecological and economic benefits.
Better Alignment with Customer Needs
By analyzing customer data, companies gain better insight into the behavior, preferences, and expectations of their target audience. This results in more personalized products and services, higher customer satisfaction, and greater loyalty. This strengthens an organization’s market position and better aligns with societal needs.
Supporting Societal Challenges
Business Intelligence also plays an increasingly important role in the public sector. Analyzing large datasets helps policymakers to understand societal trends and challenges. Think of themes like energy consumption, housing shortages, healthcare demand, or mobility. These insights enable governments, NGOs, and other stakeholders to make better-informed decisions that benefit society as a whole.
Business Intelligence with Societal Value
A Business Intelligence Specialist is therefore more than just a data analyst: they are a bridge between information and impact. By combining technology, analysis, and strategic insight, this role makes a direct contribution to societal progress. From sustainability and customer focus to policy development and innovation – the relevance of this function grows every day.

Case Study: The Role of Business Intelligence Specialist
Case Study: How TechFlare Transformed Its Decision-Making with Business Intelligence
Background
TechFlare is a fast-growing software company known for its innovative solutions across various sectors. With a broad client portfolio and an expanding range of digital services, the company generated large amounts of data on a daily basis. Although this data held a goldmine of insights, it was barely utilized. In a market where speed and precision make the difference, the need for data-driven management grew by the day.
TechFlare's management realized that intuitive decisions were no longer sufficient. To maintain a competitive edge, a foundation needed to be laid for structured, data-based decision-making.
The Challenge
TechFlare faced a classic data struggle: there was no lack of data, but there was a lack of structure and usability. Data came from various systems — from CRM to support tools and from marketing dashboards to financial reports — but there was no central location where this data was consolidated or analyzed. Employees worked based on assumptions or outdated reports.
The result? Delays in decision-making, inefficiency within teams, and an unclear picture of actual performance. Opportunities were missed simply because there was no insight into customer behavior, market trends, or operational bottlenecks.
The Breakthrough: The Arrival of a Business Intelligence Specialist
This changed with the arrival of Joris, an experienced Business Intelligence Specialist. He began by mapping the existing data landscapes and spoke with various departments to clarify their information needs. Where were the questions? Where were things going wrong? And most importantly: what did people actually want to know?
Joris then designed a robust and scalable BI framework. He connected various data sources, defined relevant KPIs, and developed intuitive dashboards that provided instant insight into performance and trends. Joris also laid the groundwork for a data culture: he organized training sessions for team leaders, marketers, product owners, and sales professionals so they could learn to interpret and apply the data themselves.
Instead of complex Excel files or months-old reports, each department gained real-time access to current and reliable management information.
The Result: From Data Chaos to Data Power
The impact was significant. Within three months, decision-making at the management level had demonstrably improved: strategies were better substantiated, investments made with greater focus, and campaigns deployed more efficiently. Operational teams reported less waste of time and resources. Customer inquiries could be answered faster because support teams now had immediate insight into relevant customer data.
The staff also noticed the difference. The new BI tools gave them more control over their work and increased engagement. A sense of control and ownership emerged, reinforced by the new insights. No longer was work based on gut feeling, but on facts.
Thanks to Joris's efforts as a Business Intelligence Specialist, TechFlare became a textbook example of how data can be used intelligently. He not only brought structure to the data but also brought people along in the story. His contribution laid the foundation for a culture where data is no longer a byproduct but a strategic asset.
Conclusion
This case demonstrates that successful digital transformation is not just about technology but above all about people, processes, and vision. The combination of technical expertise, empathy for the organization, and clear communication made the difference. The role of a Business Intelligence Specialist, like Joris, is indispensable: he acts as a bridge between raw data and smart decisions. Thanks to his approach, TechFlare not only improved its performance but also strengthened its position in a competitive market.

Vacancies for Business Intelligence Specialists
View current job openings on DataJobs.nl
Looking for a Business Intelligence Specialist?
For a small fee, you can easily post your job vacancies on our platform and reach our large, relevant network of data and analytics specialists. Applicants respond directly to you, without any third-party involvement.
On DataJobs.nl, we connect supply and demand in the data and analytics job market directly—without intermediaries. You won’t find any vacancies from recruitment agencies on our site. Visitors can view all vacancies for free and without an account, and apply directly.
See the options for posting vacancies here. Questions? Contact us!

Op zoek naar een uitdaging in data & analytics?
Bekijk hier alle actuele kansen! See vacancies- What does a Business Intelligence Specialist do
- Job Profile of a Business Intelligence Specialist
- A day in the life of a Business Intelligence Specialist
- Which tools does a Business Intelligence Specialist use
- What does a Business Intelligence Specialist earn
- Career Path and Growth Opportunities as a Business Intelligence Specialist
- Training and Certification for Business Intelligence Specialists
- Networking and Industry Organizations
- Impact and societal relevance
- Case Study: The Role of Business Intelligence Specialist
- Vacancies for Business Intelligence Specialists
- Looking for a Business Intelligence Specialist?