What Does an HR Analytics Specialist Do?
An HR Analytics Specialist plays an increasingly important role in modern organizations. In an era where data is central, this specialist helps translate large volumes of HR data into actionable insights. Think of data on turnover, absenteeism, engagement, recruitment, diversity, and performance. Through smart analyses, organizations can better manage their people strategies and support strategic decisions with facts.
What does an HR Analytics Specialist do?
An HR Analytics Specialist is responsible for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting HR-related data. The goal? Enabling data-driven decisions that contribute to a more effective, fair, and future-proof HR policy. These professionals combine analytical skills with a solid understanding of HR processes and organizational challenges.
Key tasks and responsibilities
- Collecting, cleaning, and structuring HR data from various sources such as HR information systems, surveys, and absenteeism reports.
- Developing and maintaining HR dashboards and reports that provide real-time insights into critical HR KPIs.
- Analyzing trends, correlations, and anomalies in data related to, for example, turnover, satisfaction, and internal mobility.
- Providing recommendations for improvements in HR policy, based on data insights.
- Collaborating with HR teams, management, and other stakeholders to turn data analyses into concrete actions.
- Evaluating HR initiatives based on predefined performance indicators and effectiveness.
- Applying predictive analytics to detect future risks such as unwanted turnover or burnout at an early stage.
Why is HR Analytics so important?
Insight into HR data enables organizations to implement objective and evidence-based policies. HR Analytics helps organizations optimize their workforce strategy, improve employee satisfaction, and reduce costs. By recognizing patterns early, preventive measures can be taken, directly contributing to the organization’s success.
The future of HR Analytics
The role of the HR Analytics Specialist is evolving rapidly. There is a growing demand for professionals who, in addition to data analysis, also have skills in data visualization, storytelling, and ethics. Moreover, the importance of AI and machine learning in HR is increasing, allowing predictions to become more accurate. Organizations that invest in this are building a more agile and resilient future.

Job Profile of an HR Analytics Specialist
What Does an HR Analytics Specialist Do?
An HR Analytics Specialist – also known as an HR Data Analyst or People Analyst – plays an increasingly important role within modern HR departments. This specialist helps organizations support strategic decisions with data about human capital. By analyzing HR data, insights can be gained into turnover, absenteeism, employee satisfaction, performance, and diversity.
A typical job profile of an HR Analytics Specialist includes:
- A relevant academic degree, such as human resources, business administration, psychology, sociology, statistics, or a related field. Increasingly, a background in data science or econometrics is also required.
- Experience in collecting, structuring, and analyzing HR data. Think of data from HR information systems (HRIS), absence records, feedback tools, or employee surveys.
- Familiarity with statistical analysis methods and applying models such as regression analysis, clustering, machine learning, or predictive models to identify trends and patterns.
- Knowledge of HR processes such as recruitment, onboarding, development, retention, and talent management, as well as an understanding of HR systems and relevant privacy laws and regulations (such as GDPR).
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills, with attention to detail and the bigger picture.
- Excellent communication skills, both verbal and written. The specialist must be able to present complex data insights in an understandable way to HR managers, executives, and other stakeholders.
- Experience with data analysis tools such as Excel, R, Python, or SAS. Tools like Power BI, Tableau, and SQL are also often part of the daily work.
- Skill in visualizing data and building dashboards that provide insight into key HR KPIs.
- Curiosity, critical thinking, and a proactive attitude when translating data into concrete actions and recommendations.
The Impact of HR Analytics on Organizations
By using HR Analytics, organizations can better anticipate staffing needs, plan more strategically, and improve the employee experience. Think of data-driven recruitment strategies, predicting turnover, or measuring the impact of leadership and training on performance.
HR Analytics is no longer a ‘nice to have’ but an essential part of modern talent management. Organizations that bring this expertise in-house are building a future-proof HR policy based on facts rather than assumptions.

Which tools does an HR Analytics Specialist use?
HRIS (Human Resources Information System)
HRIS systems are essential tools for HR Analytics Specialists. They serve as the central hub for collecting, managing, and analyzing employee data. Modern HRIS solutions like Workday, SAP SuccessFactors, BambooHR, and ADP not only support payroll and leave management but also offer dashboards, reporting features, and integrations with other analytics tools. This enables HR teams to make faster, data-driven decisions, which is crucial in a competitive job market.
Survey Tools for Employee Satisfaction and Engagement
To measure the employee experience, HR Analytics Specialists frequently use survey tools. Platforms like SurveyMonkey, Qualtrics, and Google Forms are used for employee satisfaction surveys, onboarding evaluations, 360-degree feedback, and pulse surveys. The collected data helps improve workplace culture, reduce turnover, and increase engagement. Thanks to advanced analytics features, these tools quickly provide insight into trends and areas of concern within teams or departments.
Data Visualization Tools for HR Dashboards
Data visualization is essential for clearly communicating insights from HR data. Tools like Tableau, Power BI, Looker, and Qlik enable HR Analytics Specialists to build interactive dashboards. These dashboards visually present trends related to turnover, absenteeism, diversity, or performance to HR managers and executives. Visual dashboards help drive swift and targeted action based on up-to-date data.
Advanced Data Analytics Software
For deeper analyses, HR Analytics Specialists use powerful statistical software. Languages and tools like R, Python, and SPSS offer extensive capabilities for regression analyses, clustering, forecasting, and machine learning. These insights are valuable for strategic HR challenges such as retention predictions, workforce planning, and improving recruitment processes.
Data Warehousing and Integration Platforms
With the growth of HR data from various sources — such as applicant tracking systems, performance review tools, and e-learning platforms — data warehousing is becoming increasingly important. Tools like Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, Snowflake, and Microsoft Azure Synapse make it possible to collect, combine, and analyze all this data in one environment. This provides a 360-degree view of the employee, which is valuable for integrated HR analytics and strategic decision-making.
Project Management Tools for HR Analytics Initiatives
Project management tools like Trello, Asana, and Jira help HR Analytics Specialists structure their work. Whether implementing a new dashboard, conducting a data analysis project, or coordinating an employee survey, these tools provide clarity, task distribution, and transparency in the process. They promote collaboration between HR, IT, and management, which is essential for data-driven projects.
Excel and Google Sheets as Basic Tools
Despite the rise of advanced analytics tools, Excel and Google Sheets remain indispensable. They are widely used for cleaning and preparing data, performing quick calculations, and creating clear tables and charts. Thanks to new features like Power Query (Excel) and AppSheet (Google), these tools are increasingly evolving into ‘low-code’ analytics solutions, making them suitable for more advanced applications as well.
AI and Machine Learning Tools (Emerging)
A recent development in the field of HR Analytics is the use of AI tools for predictive analytics and natural language processing. This includes solutions that can predict turnover based on historical data or automatically analyze open feedback for sentiment and themes. Although still emerging, platforms like IBM Watson, Google AutoML, and Microsoft Azure AI are already being cautiously explored in larger organizations.

A Day in the Life of an HR Analytics Specialist
08:30 – The day starts with data
The workday of an HR Analytics Specialist often begins with a fresh cup of coffee and the opening of dashboards. On three screens at once, real-time data appears on turnover rates, absenteeism percentages, internal mobility, and engagement. With a sharp eye, the specialist scans for anomalies or trends. Is absenteeism in the production department higher than usual? Is engagement declining in a specific business unit? This first hour is all about spotting and orienting.
09:30 – Interpreting and analyzing data
After the initial overview comes the deep dive. Using Python, R, or Power BI, the specialist digs deeper into the data. Statistical models and predictive algorithms help uncover the causes behind trends. Is there a link between employee engagement and the type of leadership in a team? Are there departments where turnover is consistently too high? These insights are carefully documented and translated into understandable visualizations.
11:00 – Collaborating with HR teams
Armed with the analyses, the specialist joins a meeting with HR Business Partners. The figures are explained in plain language. Dialogue is crucial: what do the data say, but also what don’t they say? Sometimes the numbers confirm a gut feeling; sometimes they are completely surprising. Together, follow-up actions are considered: a targeted intervention, additional research, or a new report.
12:30 – Lunch and informal exchange
During lunch in the company cafeteria or outside on the terrace, informal discussions often continue. New questions arise, for example about the effectiveness of an onboarding program or the impact of hybrid work. These conversations provide valuable input for future analyses.
13:30 – Data quality and model maintenance
The afternoon is dedicated to the quieter but crucial part of the work: data quality. The specialist ensures that personnel data is accurate, up-to-date, and usable. Incorrect or missing values are cleaned up, definitions are harmonized, and datasets are prepared for analysis. Sometimes work is done on maintaining a predictive model, for example around absenteeism or turnover, or on optimizing a new dashboard.
15:30 – Projects and strategy
In a working session with the HR director or management team, the specialist discusses ongoing projects and strategic direction. What insights has HR Analytics delivered? What are the priorities for the next quarter? Think of topics like diversity & inclusion, sustainable employability, or internal mobility. Here, data truly has impact: it influences policy and decision-making.
17:00 – Continuing to learn
The day often ends with an hour dedicated to personal development. An online training on new AI tools, an article about people analytics trends, or an internal knowledge-sharing session with other analysts. In this fast-changing field, continuous learning is essential to remain relevant and valuable.
18:00 – Wrapping up and looking ahead
After a day full of analyses, meetings, and new insights, the HR Analytics Specialist shuts down the laptop. Often with a sense of satisfaction: today, decisions were backed by data, policies improved, and perhaps even careers positively influenced – all thanks to data.

What does an HR Analytics Specialist earn?
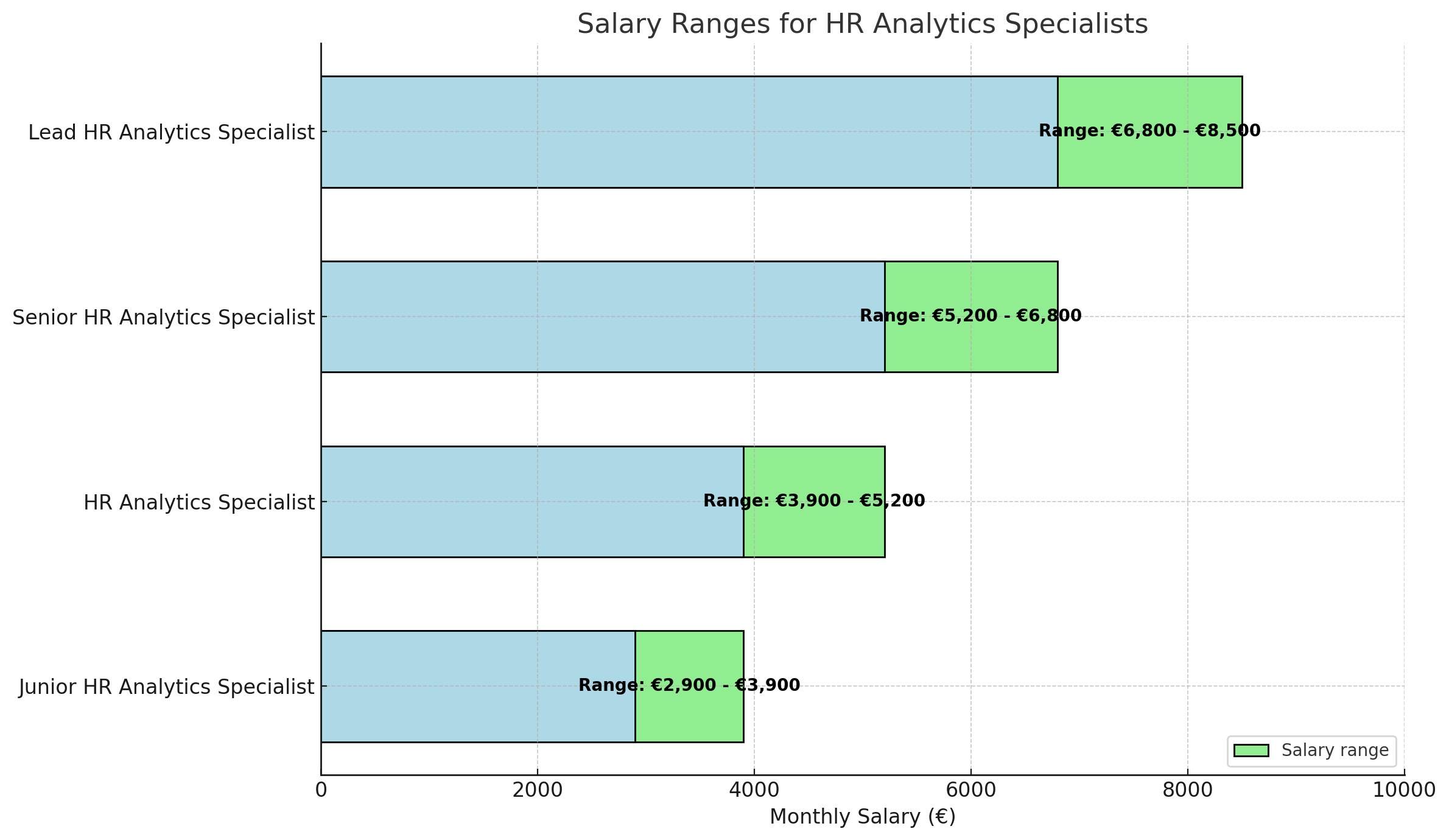
The salary of an HR Analytics Specialist varies depending on factors such as experience, location, sector, and the size of the organization. HR Analytics Specialists play an increasingly important role in translating HR data into strategic insights that contribute to better decisions regarding personnel policy, retention, recruitment, and organizational development. Below is an overview of salary expectations based on different experience levels.
Entry Level (Junior HR Analytics Specialist)
A Junior HR Analytics Specialist, often with a background in HRM, psychology, business administration, or data analysis, typically earns between €2,900 and €3,900 per month. At this stage, the focus is primarily on supportive tasks such as collecting, cleaning, and reporting HR data. They often work with systems like Excel, HRIS software, and possibly dashboard tools like Power BI or Tableau. There is usually close collaboration with HR advisors and recruitment teams.
Mid-level (HR Analytics Specialist)
An HR Analytics Specialist with 2 to 5 years of experience earns on average between €3,900 and €5,200 per month. At this level, they are independently responsible for conducting analyses on topics such as staff turnover, absenteeism, engagement, and diversity. Dashboards are also built, and HR reports are developed for management. They work with more advanced tools and statistical software, such as Python, R, or SPSS.
Senior Level (Senior HR Analytics Specialist)
A Senior HR Analytics Specialist with more than 5 years of experience earns on average between €5,200 and €6,800 per month. These professionals have in-depth knowledge of people analytics, predictive modeling, and data-driven HR strategies. They work closely with HR leadership, executives, and other departments to provide insights that contribute to organizational change and strategic HR policy. They often also mentor colleagues or act as sparring partners for HR Business Partners.
Lead or Strategic HR Analytics Specialist
In larger organizations or consultancy roles, there is the position of Lead HR Analytics Specialist or Strategic HR Analytics Expert. These specialists can earn between €6,800 and €8,500 per month. They are responsible for the direction and implementation of HR analytics policy, lead analytics projects, develop KPI frameworks, and advise top management on topics such as workforce planning and organizational development.
Location and Sector
Salaries for HR Analytics Specialists are generally higher in regions with a strong presence of multinationals, such as Amsterdam, Utrecht, and The Hague. Sectors such as consultancy, financial services, healthcare, and technology typically offer better compensation packages, partly due to the strategic role HR analytics plays in those sectors. International organizations with a data-driven HR vision also often offer more growth opportunities and higher salaries.
Education and Skills
The background and skills of an HR Analytics Specialist have a significant impact on salary. A master’s degree in HRM, psychology, data science, or econometrics is often a plus. Additionally, skills such as statistical analysis, data visualization, storytelling with data, and knowledge of tools like SQL, Power BI, Python, or Workday increase market value. Knowledge of privacy legislation (GDPR) and ethics in data analysis is also becoming increasingly important in this role.
Career Path and Growth Opportunities as an HR Analytics Specialist
Career Path and Growth Opportunities as an HR Analytics Specialist
A Dynamic Career Path in a Data-Driven HR Environment
A career as an HR Analytics Specialist offers excellent prospects for professionals who want to leverage the power of data to enhance people-oriented decision-making. In this role, you combine analytical insight with knowledge of HR processes, making you indispensable in modern organizations aiming for evidence-based HR policies.
Growth Opportunities: From Specialist to Strategic Partner
As you gain more experience and refine your skills in data visualization, predictive analytics, and storytelling with HR data, you can advance into various senior roles. These include positions such as:
- Senior HR Analytics Specialist: with more responsibility for complex analyses and project leadership;
- HR Analytics Manager: focusing on leading an analytics team and developing a data strategy for HR;
- HR Business Partner: combining analytics with strategic-level consulting for management and leadership;
- Head of People Analytics: where you're responsible for the entire data and analytics vision within HR.
Specialization Within the HR Analytics Domain
As an HR Analytics Specialist, you can also dive deeper into specific areas within HR. Popular specializations include:
- Talent Management: analyzing the inflow, progression, and outflow of talent to support strategic decisions;
- Diversity and Inclusion: measuring and improving inclusive HR practices based on data insights;
- Employee Relations and Engagement: using surveys, feedback loops, and predictive models to enhance employee engagement and satisfaction.
Growing Demand in the Job Market
The demand for HR Analytics Specialists is steadily increasing. More and more organizations recognize that data-driven HR contributes to better decisions regarding personnel, culture, and organizational development. As a result, there are not only more job openings but also more opportunities to shape your role and grow within it.
Conclusion: A Career with Impact and Future Prospects
As an HR Analytics Specialist, you operate at the intersection of data, technology, and human capital. It's a role that is becoming increasingly important and offers plenty of opportunities for further development, both in-depth and toward leadership. Whether you choose to specialize in a niche or broaden your scope toward strategic roles: the future of HR is data-driven – and you can play a key role in it.

Training and Certification for HR Analytics Specialists
To be successful as an HR Analytics Specialist, it's essential to continuously invest in your knowledge, skills, and professional development. The world of HR Analytics is evolving rapidly, with new tools, technologies, and insights constantly emerging. In addition to a relevant academic background, such as a degree in business administration, HRM, psychology, or data science, there are various specialized courses and certifications available to help you stand out in this field.
Why certification in HR Analytics?
Earning a certification demonstrates that you have the right expertise to turn HR data into valuable insights. It strengthens your position in the job market and increases your chances of landing interesting projects or roles. For employers, a certified HR Analytics Specialist is often reassuring: they know you have up-to-date knowledge and practical skills.
Popular certifications and courses
Below is an overview of some highly sought-after certifications that can enhance your career as an HR Analytics Specialist.
HR Analytics Professional Certificate
This certification focuses on the methods, tools, and techniques needed to effectively analyze and interpret HR data. Topics include data quality, dashboards, statistical analysis, and data storytelling. This course is suitable for HR professionals who want to strengthen their analytical skills and work more data-driven.
People Analytics Certificate
This program dives deeper into using analytics to measure and improve the impact of HR initiatives. Topics such as employee engagement, staff turnover, diversity, and performance analysis are covered. This certification is ideal for HR professionals who want to embrace evidence-based HR and demonstrate the added value of their policies.
Certified Talent Management Analyst
This certification offers an in-depth focus on using data analysis in talent management processes. From recruitment and selection to performance reviews and career development: this course teaches you how to leverage data to optimize these processes. You'll also learn how to apply predictive models to forecast future staffing needs.
Emerging trends and additional training
More and more courses are addressing topics such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics in HR. There's also growing interest in ethics and privacy when using HR data. In addition, soft skills like data storytelling and stakeholder management are becoming increasingly important in training programs for HR Analytics specialists.
Benefits of certification
- Strengthen your position in the job market
- Increase your credibility within HR teams and leadership
- Stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and insights
- Learn how to apply HR analytics strategically within organizations

Become a future-ready HR Analytics Specialist
By taking targeted courses and earning recognized certifications, you show potential employers and clients that you possess up-to-date knowledge and applicable skills. You contribute to the effectiveness and strategic value of HR within the organization. The investment in training and certification quickly pays off in the form of better opportunities, greater impact, and a stronger professional reputation.
Networking and Industry Associations
Industry Associations: Increase Your Impact and Visibility
For HR Analytics Specialists, it is essential to stay actively engaged in professional networks and industry associations. Not only to stay up to date with the latest developments and best practices in HR data analysis, but also to position yourself as an expert in the field. Membership in leading organizations such as the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) or the HR Metrics & Analytics Association provides access to valuable resources, research, whitepapers, and exclusive events.
Attending industry conferences, seminars, and themed meetups allows you to connect directly with other professionals, thought leaders, and decision-makers in HR and analytics. By actively participating in these networks — for example, by contributing to working groups or panels — you not only expand your knowledge but also increase your visibility in the market. This can ultimately lead to interesting career opportunities, consultancy projects, or strategic collaborations.
Online Communities and Platforms
In addition to physical networks and organizations, online platforms offer an accessible way to share knowledge and expand your network. LinkedIn groups, specialized Slack channels, HR data forums, and communities like Reddit and GitHub (for more technical aspects of data analysis) are valuable sources of information and exchange.
By actively participating in discussions, asking questions, sharing cases, or helping others with your expertise, you not only grow in terms of content but also build your professional reputation. This can open doors to new opportunities, such as collaborations, webinar invitations, or even speaker invitations at events.
Keep Learning, Keep Growing
The world of HR Analytics is evolving rapidly. New technologies, data products, and regulations make it necessary to keep learning continuously. Surrounding yourself with other professionals in the field — both physically and online — keeps you sharp, inspired, and future-proof.
In short: investing in your network and being an active member of industry associations is not a side activity, but a crucial part of a successful career as an HR Analytics Specialist.

Impact and Social Relevance
The Impact and Societal Relevance of the HR Analytics Specialist
A Key Role in People-Centered HR Policies
The HR Analytics Specialist plays an increasingly important role in shaping effective and people-centered HR policies. In a time when organizations face challenges such as labor shortages, diversity issues, and hybrid work models, HR analytics provides concrete insights to develop better policies. By intelligently analyzing workforce data, companies can effectively address topics such as employee satisfaction, talent development, absenteeism reduction, and retention.
Optimizing Human Capital
Data-driven HR helps organizations attract, retain, and motivate talent. By recognizing patterns in behavior and performance, an HR Analytics Specialist can make valuable recommendations that lead to a better match between employees and roles, greater job satisfaction, and increased productivity. This results in a stronger organizational culture, lower turnover, and higher engagement within teams.
Contributing to Fairness and Inclusion
The societal relevance of HR analytics lies in the ability to create fairer and more inclusive workplaces. Data analysis makes it possible to uncover and address unconscious biases and structural inequalities within HR processes. In doing so, the HR Analytics Specialist contributes to promoting equal opportunities, reducing discrimination, and enhancing diversity within organizations.
Strengthening Organizational Culture
By continuously monitoring how employees experience the organization, timely adjustments can be made to culture, leadership, and internal communication. This supports the development of a positive, safe, and stimulating work environment. A well-functioning HR analytics program thus contributes to sustainable employability and mental health in the workplace.
Societal and Economic Value
In a knowledge-driven economy, talent is at the heart of competitiveness. The HR Analytics Specialist ensures that organizations strategically leverage their human capital, with attention to both business performance and employee well-being. This role not only adds value at the organizational level but also contributes to broader societal prosperity and economic growth.
A Forward-Looking Role with Impact
The role of the HR Analytics Specialist is rapidly evolving, and more organizations are recognizing the necessity of data-driven HR. The position offers opportunities for professionals who want to connect data with human behavior and is essential in creating a modern, inclusive, and future-proof labor market.

Case Study: HR Analytics Specialist at TechCorp
Talent retention as a challenge
TechCorp, an international technology company with over 10,000 employees, was growing at lightning speed. Yet it faced a persistent problem: young professionals often left the company within two years. And this despite excellent employment conditions: a good salary, attractive secondary benefits, and plenty of career advancement opportunities. The question remained: why were they still leaving?
The HR Analytics Specialist enters the picture
To get to the root of the problem, TechCorp decided to hire an HR Analytics Specialist. This professional delved deep into the company’s workforce data. Turnover rates, performance data, feedback forms, and workload measurements were all analyzed. Striking patterns quickly emerged.
In certain teams, the turnover among young employees was significantly higher. The common factor? Structural overtime, limited access to training, and a lack of mentorship. Young talent felt insufficiently supported and overwhelmed — with departure as the logical result.
Targeted actions based on data
Armed with these insights, HR took action. A mentorship program was launched, specifically aimed at new hires. Teams experiencing high workloads received additional support, and flexible working hours were introduced to improve the work-life balance.
The results were quick to follow. Within a year, turnover among young professionals dropped by no less than 15%. Not only did employees stay longer, they also reported feeling more valued and supported in internal surveys.
Impact on the organization
This case demonstrates the power of HR Analytics. Through targeted analysis and intervention, TechCorp not only managed to retain employees longer but also strengthened its corporate culture. The HR Analytics Specialist proved to be an essential link between data and human impact.

Looking for a HR Analytics Specialist?
For a small fee, you can easily post your job vacancies on our platform and reach our large, relevant network of data and analytics specialists. Applicants respond directly to you, without any third-party involvement.
On DataJobs.nl, we connect supply and demand in the data and analytics job market directly—without intermediaries. You won't find vacancies from recruitment agencies here. Visitors can view all vacancies for free and without an account, and apply directly.
View the options for posting job vacancies here. Questions? Contact us!

Op zoek naar een uitdaging in data & analytics?
Bekijk hier alle actuele kansen! See vacancies- What Does an HR Analytics Specialist Do?
- Job Profile of an HR Analytics Specialist
- Which tools does an HR Analytics Specialist use?
- A Day in the Life of an HR Analytics Specialist
- What does an HR Analytics Specialist earn?
- Career Path and Growth Opportunities as an HR Analytics Specialist
- Training and Certification for HR Analytics Specialists
- Networking and Industry Associations
- Impact and Social Relevance
- Case Study: HR Analytics Specialist at TechCorp
- Jobs for HR Analytics Specialists
- Looking for a HR Analytics Specialist?