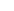What does a Web Analyst do?
A Web Analyst is a data specialist who helps organizations gain better insights into the online behavior of visitors. Using advanced analytical techniques and tools such as Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, or Matomo, the Web Analyst translates large volumes of website data into concrete improvements for online performance, usability, and conversion.
What does a Web Analyst do?
Web Analysts play a key role within digital teams. They combine analytical thinking with knowledge of online marketing and UX (user experience). Their main goal is to provide data-driven insights that help organizations optimize their digital strategy.
Key tasks and responsibilities
- Collecting and analyzing data: Think of visitor numbers, bounce rates, session duration, click behavior, traffic sources, conversion rates, and funnels.
- Trend analysis and optimization: Identifying behavior patterns and bottlenecks to detect improvement opportunities for content, campaigns, or user experience.
- Creating dashboards and reports: Results are visually presented to stakeholders using tools like Google Looker Studio or Power BI.
- Advising and collaborating: Web Analysts work closely with digital marketers, CRO specialists, UX designers, and developers to implement recommendations.
- Testing and monitoring optimizations: A/B testing, multivariate testing, and continuous monitoring are essential to measure the impact of changes.
- Managing tag management and tracking: They ensure that measurement points are correctly configured using systems like Google Tag Manager or server-side tracking.
Why is a Web Analyst important?
Without a Web Analyst, valuable insights from website and campaign data go unused. They translate data into action, which is crucial for growth, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Whether it's increasing conversions, improving the customer journey, or supporting strategic decisions—the Web Analyst is the link between technology, marketing, and business.
Skills of a successful Web Analyst
- Strong analytical skills and attention to detail
- Knowledge of web analytics tools and visualization dashboards
- Affinity with digital marketing and UX
- Experience with HTML, JavaScript, and tag management is a plus
- Good communication skills to translate insights into concrete recommendations
The future of web analytics
Due to stricter privacy regulations (such as the GDPR) and the shift to first-party data, the role of Web Analysts is evolving. Server-side tracking, cookieless measurement, and AI-driven insights are becoming increasingly important. At the same time, the demand for specialized Web Analysts is growing—companies are investing more in data-driven marketing and performance optimization.

Job Profile of a Web Analyst
Job Profile of a Web Analyst
A Web Analyst plays a crucial role in optimizing an organization's online performance. By analyzing user behavior and interpreting data, the Web Analyst provides valuable insights that lead to improved customer experience, higher conversions, and more effective digital strategies.
A modern and comprehensive job profile of a Web Analyst includes:
- A relevant academic background, such as computer science, data science, statistics, marketing, business administration, or a related field.
- Proven experience with web analysis, digital marketing, UX analysis, or online strategy, preferably in a commercial or e-commerce environment.
- In-depth knowledge of web analytics tools such as Google Analytics 4 (GA4), Adobe Analytics, Hotjar, Mixpanel, or Matomo. Familiarity with tagging via Google Tag Manager is a plus.
- Strong analytical skills: you can identify patterns and trends in large volumes of user data and translate them into concrete recommendations.
- Experience in setting up, monitoring, and interpreting A/B tests, multivariate tests, and conversion optimization.
- Familiarity with UX and web design principles, enabling collaboration with designers and developers to improve the user experience.
- Good knowledge of tools such as Excel, SQL, and preferably programming languages like Python or R for deeper analysis.
- Strong communication skills, both written and verbal. You can clearly convey complex insights to stakeholders, marketers, developers, and management.
- Understanding of KPIs and dashboards: you can independently build and maintain reports in tools such as Google Data Studio, Tableau, or Power BI.
- Affinity with privacy and data regulations, such as GDPR, and experience with implementing cookie banners and tracking policies.
Competencies and Personality
A good Web Analyst is curious, precise, and result-oriented. You have a keen eye for detail without losing sight of the bigger picture. You work independently but know how to make an impact within a multidisciplinary team.
Conclusion
The role of Web Analyst is indispensable for organizations aiming to drive online growth through data-driven approaches. With the right combination of technical skills, analytical insight, and communication strength, a Web Analyst delivers immediate value in improving digital performance.

Welke tools gebruikt een Web Analist
Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
Google Analytics is nog steeds dé basis voor webanalyse, maar de nieuwste versie – GA4 – biedt krachtigere inzichten dan ooit. Webanalisten gebruiken GA4 om gebruikersgedrag op websites en apps te volgen, inclusief interacties, gebeurtenissen, scrollgedrag en conversies. Met de ingebouwde machine learning-functionaliteiten kun je voorspellingen doen over gebruikersgedrag en segmenten automatisch herkennen. Ook het combineren van web- en appdata is nu mogelijk, wat zorgt voor een completer beeld.
Hotjar
Hotjar blijft onmisbaar voor het verkrijgen van kwalitatieve inzichten. Met visuele tools zoals heatmaps, sessieopnamen en feedback polls krijg je letterlijk te zien wat bezoekers doen en denken. Webanalisten gebruiken Hotjar om knelpunten op te sporen, conversieproblemen op te lossen en de gebruikerservaring continu te verbeteren.
Google Tag Manager (GTM)
Google Tag Manager is een slimme en flexibele oplossing voor het beheren van meetcodes op een website – zonder afhankelijk te zijn van ontwikkelaars. Webanalisten zetten GTM in om onder meer conversies, scroll-events, button-clicks en formuliervelden nauwkeurig te meten. Dankzij GTM wordt dataverzameling efficiënter én nauwkeuriger ingericht.
Looker Studio (voorheen Google Data Studio)
Looker Studio stelt webanalisten in staat om dashboards en rapporten op maat te bouwen, die automatisch updaten en eenvoudig gedeeld kunnen worden. Met deze tool verbind je datasets uit onder andere Google Analytics, Google Ads en BigQuery. De interactieve visualisaties helpen bij het presenteren van complexe data op een begrijpelijke manier – ideaal voor management en stakeholders.
SEO-tools zoals Moz, SEMrush en Ahrefs
Webanalisten kijken niet alleen naar bezoekersgedrag, maar ook naar waar die bezoekers vandaan komen. Met tools zoals Moz, SEMrush of Ahrefs worden zoekwoorden geanalyseerd, technische SEO-problemen opgespoord en backlinks geëvalueerd. Deze inzichten zijn cruciaal om organisch verkeer te verbeteren en concurrentievoordeel te behalen in zoekmachines.
Microsoft Excel en Google Sheets
Spreadsheets blijven een krachtig hulpmiddel voor het analyseren, ordenen en opschonen van ruwe data. Webanalisten gebruiken Excel en Sheets voor het maken van data-overzichten, calculaties, tijdreeksen en scenario-analyses. Met behulp van formules, draaitabellen en grafieken wordt data snel vertaald naar inzichten.
A/B-testtools zoals Optimizely of Google Optimize
Data-inzichten worden pas waardevol als ze leiden tot optimalisaties. Tools zoals Optimizely en Google Optimize worden gebruikt om A/B-testen uit te voeren. Hiermee kan een webanalist objectief bepalen welke versie van een pagina, knop of formuliertitel het beste presteert. Zo worden beslissingen genomen op basis van bewijs in plaats van onderbuikgevoel.
SQL en Python
Voor wie een stap verder wil gaan in data-analyse zijn programmeertalen zoals SQL en Python onmisbaar. SQL wordt gebruikt voor het ophalen en bewerken van grote datasets uit databases, terwijl Python uitblinkt in het automatiseren van analyses, visualiseren van data en het bouwen van voorspellende modellen. Webanalisten die deze tools beheersen hebben een flinke voorsprong op de arbeidsmarkt.
Extra tools en integraties
Afhankelijk van de organisatie en het type project kunnen webanalisten ook werken met tools zoals BigQuery voor datawarehousing, Amplitude of Mixpanel voor product analytics, of Power BI voor business intelligence-rapportages. Ook integraties met CRM-systemen, e-commerceplatforms en e-mailmarketingtools worden steeds belangrijker om een 360-graden klantbeeld te creëren.

A day in the life of a Web Analyst
A Day in the Life of a Web Analyst: Tools, Insights, and Impact
A Web Analyst is much more than just a number cruncher behind a screen. This is someone who translates the digital behavior of thousands of visitors into insights that help companies grow. From measuring scroll behavior to building dashboards, and from A/B testing to cleaning datasets—no day is the same. Below, we take you through the rhythm and tools of a typical workday.
09:00 – Start of the Day and Initial Data Check with GA4
Google Analytics 4 is the digital compass for the Web Analyst. The day often starts with a quick check: are there any noticeable drops in traffic? New spikes in conversions? In GA4, you view user behavior on both the website and the app. Scroll behavior, clicks, events—everything is tracked.
Thanks to built-in machine learning, trends and audiences are automatically detected. For example, you might see that a particular campaign is performing unexpectedly well in mobile traffic. A Web Analyst then immediately knows where to focus that day.
10:30 – Understanding the Context with Hotjar
Numbers tell you what’s happening, but tools like Hotjar show you why it's happening. With heatmaps, session recordings, and feedback polls, you can literally see visitor behavior. Is a button being ignored? Are people dropping off at a form?
Hotjar offers the qualitative complement to the hard data: the digital fingerprint of your user.
11:30 – Refining Measurements via Google Tag Manager
With Google Tag Manager (GTM), the Web Analyst fine-tunes the measurement infrastructure. Want to measure a new CTA? Or see how many people scroll halfway down a longread? Thanks to GTM, you can add tags independently without needing a developer.
This makes data collection not only more flexible but also more reliable.
13:00 – Reporting and Visualizing in Looker Studio
After lunch, it's time to share insights. In Looker Studio (formerly Google Data Studio), the Web Analyst builds dashboards that update automatically. Charts, tables, filters—visual, interactive, and understandable for everyone.
With sources like GA4, Search Console, Google Ads, and even BigQuery, you create reports that provide immediate insights to marketing teams, product managers, or executives.
14:30 – Diving into SEO Data with Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz
A Web Analyst also looks at how visitors land on the site. With tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz, you analyze keywords, discover backlinks, and detect technical SEO issues.
Based on these insights, you make recommendations to improve organic traffic—from content adjustments to technical optimizations.
15:30 – Manipulating Data in Excel or Google Sheets
For quick calculations, cleaning data, or creating time series, Excel or Sheets remains indispensable. Pivot tables, formulas, charts—with just a few formulas, insights emerge quickly.
These tools often serve as the bridge between raw data and final reports or dashboards.
16:15 – Testing Hypotheses via A/B Testing Tools
Data leads to action. With Google Optimize or Optimizely, you test variations of pages or buttons: what converts better? A different image? Shorter forms? The Web Analyst sets up an A/B test, defines success criteria, and monitors the results objectively.
No guesswork—only decisions based on evidence.
17:00 – Going Deep with SQL and Python
For complex analyses or automated processes, the Web Analyst turns to SQL and Python. SQL is used to retrieve large datasets, and Python for predictive models and data visualizations.
Those who master these languages are well-equipped in any data-driven team.
17:45 – Wrapping Up with Tools & Integrations
Before the day ends, the Web Analyst often checks additional systems: BigQuery for data warehousing, Amplitude or Mixpanel for product analytics, and Power BI for BI reporting. Additionally, data is linked to CRMs or e-commerce platforms to enrich the customer profile.

18:00 – Day Concluded, Insights Sown
A Web Analyst is not a number cruncher, but a digital detective. Someone who connects the dots with the right tools, detects bottlenecks, and makes real impact with smart dashboards and recommendations. The combination of technical knowledge, analytical skills, and communication power makes this profession unique—and indispensable in the digital age.
Wat verdient een Web Analist
The salary of a Web Analyst varies depending on experience, location, sector, and the size of the organization. Web Analysts play a key role in analyzing user behavior on websites and apps. They translate data into concrete recommendations that help improve digital performance. Below is an overview of salary expectations for Web Analysts at different experience levels.
Entry Level (Junior Web Analyst)
A Junior Web Analyst, often a recent graduate in fields such as marketing, communications, computer science, or data analysis, typically earns between €2,800 and €3,800 per month. In this role, they primarily perform operational tasks such as setting up tracking in Google Tag Manager, creating dashboards in Looker Studio, and analyzing user data in GA4. Juniors often work closely with more experienced analysts or marketers and build experience with tools like Hotjar, Excel, and basic SQL.
Mid-level (Web Analyst)
A Web Analyst with 2 to 5 years of experience generally earns between €3,800 and €5,000 per month. At this level, the analyst is capable of independently conducting web analyses, setting up A/B tests, and identifying and improving conversion issues. The Web Analyst translates user data into optimizations for the website or app and presents insights to marketing teams, UX designers, or product managers. Proficiency in tools such as GA4, GTM, Looker Studio, SQL, and Python is often required.
Senior Level (Senior Web Analyst)
A Senior Web Analyst with more than 5 years of experience earns between €5,000 and €6,500 per month. This professional has in-depth knowledge of conversion optimization, user behavior, and data visualization. Senior Web Analysts often lead strategic optimization projects, proactively advise stakeholders, and combine data from multiple sources (such as GA4, CRM systems, and e-commerce platforms) to create a holistic customer view. They often have a leadership role in the team and mentor junior analysts.
Lead Web Analyst
The role of Lead Web Analyst is mainly found within large or data-driven organizations. This position comes with managerial and strategic responsibilities. The salary typically ranges between €6,500 and €8,000 per month. The Lead Web Analyst manages a team, oversees the data strategy for digital channels, and collaborates closely with departments such as UX, IT, and marketing automation. These professionals are often experts in tools such as BigQuery, Mixpanel, Power BI, and predictive analytics.
Location and Sector
Salaries for Web Analysts in the Randstad region (Amsterdam, Utrecht, Rotterdam, The Hague) are often higher than in the rest of the Netherlands. Many large digital agencies, e-commerce companies, and international tech firms are located there. The industry also matters: sectors like finance, e-commerce, and technology usually offer higher salaries than education or non-profit. Additionally, organizations that prioritize digitalization or data-driven work typically offer more attractive conditions.
Education and Skills
The background and skillset of a Web Analyst have a major impact on salary level. A degree in marketing analytics, (digital) communications, computer science, or data science is often preferred. Skills in tools such as GA4, Google Tag Manager, Looker Studio, SQL, Python, Amplitude, Mixpanel and A/B testing tools like Optimizely increase the chances of a higher salary. Experience with UX, conversion optimization, and data visualization (e.g., with Power BI or Tableau) is also a plus.
Career path and growth opportunities as a Web Analyst
A career as a Web Analyst is not only intellectually engaging but also offers ample growth opportunities. Web analysis is a constantly evolving field due to technological innovations, changing consumer behavior, and the increasing role of data in decision-making. As a Web Analyst, you can shape and deepen your career in various ways.
Advancing to senior or leadership roles
As you gain more experience and further develop your analytical skills, you can move into roles such as Senior Web Analyst, Team Lead Digital Analytics, or Web Analytics Manager. In these positions, you not only guide analytical work but also manage fellow analysts and provide strategic advice at a higher level. The role of Digital Marketing Manager is also an option, where you bridge the gap between data and marketing strategy.
Specializing in a niche within web analytics
The role of Web Analyst is broad but also offers room for specialization. You can focus on specific domains such as:
- SEO analysis – focused on optimizing organic website traffic.
- Social media analysis – gaining insights into user behavior and preferences on social platforms.
- E-commerce analysis – improving conversion rates and customer journeys in online shops.
- CRO (Conversion Rate Optimization) – increasing conversion rates through data analysis and A/B testing.
- Customer journey analytics – mapping the full customer journey across various channels.
Horizontal growth and broadening
Not all growth is vertical. Many Web Analysts broaden their profiles toward roles like Data Analyst, Digital Consultant, or even Product Owner in digital teams. This allows you to stay closely involved in the development of digital strategies while having a broader impact on the overall process.
Continuous learning and certification
To enhance your career opportunities, it’s advisable to keep your knowledge up to date through training and certifications. Think of Google Analytics 4, Google Tag Manager, Data Studio/Looker, SQL, Python, and tools like Adobe Analytics or Hotjar. Knowledge of UX, AI, and data visualization is also becoming increasingly valuable.
Future outlook as a Web Analyst
With increasing digitization and data-driven decision-making, the demand for Web Analysts remains strong. Employers seek professionals who can not only gather data but also translate it into actionable insights. This field offers not just immediate opportunities, but long-term prospects as well.

Education and Certification for Web Analysts
Want to be successful as a Web Analyst? Then it’s essential to continuously invest in your knowledge, skills, and professional development. The world of web analytics is evolving rapidly, with new tools, technologies, and insights emerging constantly. In addition to a relevant academic background in fields such as marketing, data science, or communications, you can stand out by pursuing targeted courses and certifications. Below is an overview of the most important and up-to-date certifications for web analysts.
Google Analytics Certification (GA4)
Since the transition from Universal Analytics to Google Analytics 4 (GA4), the certification program has been updated. The Google Analytics Certification via Skillshop is now fully focused on GA4. The course covers topics such as event-based data collection, setting up conversions, building reports, and interpreting user behavior. This certification is ideal for both beginner and experienced web analysts working within Google’s ecosystem.
Adobe Analytics Business Practitioner Expert
The Adobe Analytics Business Practitioner Expert certification is designed for professionals who want to gain in-depth knowledge of analyzing data with Adobe Analytics. You’ll learn how to build segments, configure dashboards, and turn insights into actionable optimizations. This certification is especially relevant for analysts working in large enterprise environments.
Digital Analytics Association (DAA) Certified Web Analyst
The Certified Web Analyst certification from the Digital Analytics Association is internationally recognized and highly comprehensive. The exam tests you on topics such as data quality, tag management, analysis processes, visualization, and ethics. This certification is suitable for experienced web analysts who want to demonstrate their expertise at a strategic level.
Conversion Optimization & UX Analysis Course
In addition to technical web analysis, there is growing demand for professionals who can translate data into concrete improvements. Courses in conversion optimization and UX analysis teach you how to analyze customer behavior using data, identify pain points, and implement optimizations. This type of training is often offered by specialized educational institutions and is a valuable addition for web analysts aiming to make an impact.
Tag Management & Tracking Fundamentals
For accurate data collection, knowledge of tag management is essential. Courses on Google Tag Manager, server-side tracking, and consent management ensure your data collection is reliable, GDPR-compliant, and efficiently set up. This knowledge forms the technical foundation of every successful web analysis.

By investing in relevant certifications and training, you demonstrate to employers and clients that you possess up-to-date knowledge and practical skills. You not only increase your job security but also your value as a professional in the labor market. As a web analyst, you are the link between data and digital growth — and with the right training, you’re ready for the future.
Networking and industry associations
Industry Organizations and Networks
For anyone serious about building a career in web analytics, it's essential to be actively involved in relevant industry organizations and professional networks. These organizations not only provide access to valuable knowledge and tools, but also serve as platforms for professional development and visibility. Consider, for example, the Digital Analytics Association (DAA) and the Web Analytics Demystified network. These help you stay up to date with the latest trends, benchmarks, and best practices in digital analytics.
By attending conferences, seminars, and trade fairs, you meet other professionals, exchange experiences, and gain new insights that can be directly applied to your work. In addition, participating in working groups, committees, or mentorship programs within these organizations gives you the chance to actively contribute to the development of the field. This strengthens your profile as an expert and opens doors to new career opportunities.
In the Netherlands too, there are an increasing number of initiatives and networks for digital analytics professionals. Think of specialized meetups, knowledge sessions, or professional days on topics such as privacy in analytics, data storytelling, and conversion optimization. By making yourself visible in these kinds of networks, you increase your chances of interesting projects, valuable collaborations, and future jobs.
Online Networks and Communities
In addition to physical networks, there are also numerous digital platforms where, as a Web Analyst, you can join discussions, showcase your expertise, and make new contacts. Think of forums, LinkedIn groups, and specialized communities where current issues are discussed daily and knowledge is shared. Examples include the Google Analytics Help Forum, the Adobe Analytics Community Forum, and the Digital Analytics Association (DAA) LinkedIn Group.
These online communities are ideal for easily asking questions, sharing insights, or picking up the latest updates on tools, legislation, or techniques. You'll stay informed about where the sector is heading and can position yourself as an active and engaged professional.
Building an online network also brings direct benefits to your career: from inspiring collaborations to valuable job opportunities that come your way through word of mouth. Those who are consistently visible and participate in conversations are recognized more quickly as experts – and are offered more opportunities.

Impact and societal relevance
The Societal Impact of the Web Analyst
In the digital age, the Web Analyst plays an indispensable role. This professional is responsible for collecting, interpreting, and translating user data into insights that directly contribute to the improvement of websites and digital applications. By analyzing visitor behavior—such as click patterns, interaction flows, and conversion paths—the Web Analyst helps organizations continuously optimize their online strategy.
Enhancing the User Experience
One of the most important contributions of the Web Analyst is improving the user experience. By identifying where visitors drop off or encounter obstacles, companies can make targeted adjustments that enhance usability and accessibility. This results in quicker interactions, more satisfied users, and higher conversions. In a world where more and more consumers make purchases, gather information, and communicate online, a smooth digital experience is essential.
Digital Inclusion and Security
The insights of a Web Analyst also contribute to digital inclusion. By identifying which user groups struggle with navigation or content access, platforms can better respond to the needs of diverse audiences—such as seniors, people with visual impairments, or users with limited digital skills. Additionally, data analysis helps detect suspicious or unwanted activity, strengthening digital security and trust in online services.
Encouraging Fair Competition
A well-trained Web Analyst enables organizations to continuously improve their performance based on objective data. This promotes fairer competition, as not only large companies with big budgets can innovate, but also smaller businesses can adjust and optimize their strategies. This creates more equal opportunities in the digital economy, leading to innovation and a healthy market dynamic.
Strengthening the Digital Economy
On a macro level, the Web Analyst makes a significant contribution to the growth and resilience of the digital economy. By helping companies operate more efficiently and think more customer-focused, more sustainable business models emerge. The continuous optimization of digital processes also leads to cost savings, reduced waste, and more value for both companies and consumers.
Increasing Societal Importance
The societal relevance of the Web Analyst is growing by the day. In a society that is increasingly dependent on digital technology, it is crucial that online platforms are reliable, user-friendly, and fair. The Web Analyst acts as a bridge between technology and human need—playing a key role in the future of digital society.

Case Study: The Web Analyst at TechShop B.V.
Case Study: Conversion Increase through the Use of a Web Analyst
Introduction
TechShop B.V., a rapidly growing e-commerce platform with a wide range of consumer electronics, was at a crossroads. Although the website attracted thousands of visitors daily, the conversion rate – the number of visitors who actually made a purchase – lagged behind expectations. Management therefore decided to bring in a specialized Web Analyst. Goal: to thoroughly analyze website visitor behavior and uncover optimization opportunities.
Analysis and Discovery
As soon as the Web Analyst joined the team, he began with an extensive data analysis. He used tools such as Google Analytics, Hotjar, and Google Tag Manager to fully map the user journey – from entry to potential purchase.
Patterns quickly emerged. A heatmap analysis, for example, showed that visitors often lingered on product pages but rarely clicked through to the shopping cart. And those who did often dropped off noticeably on the checkout page. Scroll and click data revealed that users struggled to enter their information, and unclear error messages caused frustration.
The Web Analyst concluded that the checkout page was a bottleneck in the customer journey: cluttered, not mobile-friendly, and with too many mandatory fields. These insights formed the basis for the next step.
Action and Implementation
Based on his findings, the Web Analyst drew up a concrete action plan. He collaborated with UX designers and developers to design a new, simplified checkout page. Key adjustments included:
- Minimizing the number of input fields;
- Adding visual progress bars to reassure users;
- Optimizing the mobile display;
- And adding clear error messages with suggested solutions.
In addition, a series of A/B tests were set up to compare different versions of the checkout page. This allowed for an objective assessment of which elements positively influenced the conversion rate.
Result
Within a few weeks of implementation, the results became visible. TechShop B.V. saw an impressive 15% increase in the conversion rate, without additional marketing costs. The bounce rate on the checkout page also dropped by nearly 20%.
Customer feedback through reviews and satisfaction surveys showed a clear improvement: phrases like “finally ordered smoothly” and “much more user-friendly than before” appeared regularly.
The collaboration with the Web Analyst proved to be a bullseye. His data-driven approach translated into tangible gains—not only in numbers but also in customer satisfaction and ease of use. For TechShop B.V., this meant not only an increase in revenue but also a stronger online reputation and a solid foundation for further growth.

Vacancies for Web Analysts
View all current job openings on DataJobs.nl
Looking for a Web Analyst?
For a small fee, you can easily post your vacancies on our platform and reach our large, relevant network of data and analytics specialists. Applicants respond directly to you, without any third-party involvement.
On DataJobs.nl, we connect supply and demand in the data and analytics job market directly—without intermediaries. You won’t find any recruitment agency vacancies here. Visitors can view all job listings for free, without an account, and apply directly.
See the options for posting vacancies here. Questions? Contact us!

Op zoek naar een uitdaging in data & analytics?
Bekijk hier alle actuele kansen! See vacancies- What does a Web Analyst do?
- Job Profile of a Web Analyst
- Welke tools gebruikt een Web Analist
- A day in the life of a Web Analyst
- Wat verdient een Web Analist
- Career path and growth opportunities as a Web Analyst
- Education and Certification for Web Analysts
- Networking and industry associations
- Impact and societal relevance
- Case Study: The Web Analyst at TechShop B.V.
- Vacancies for Web Analysts
- Looking for a Web Analyst?